原题链接:点这儿。
网易的题还是有技术含量的,二分和数学和优美暴力考察得较多,这些东西在工作中确实很重要,都是优化程序的方法。
第一题:牛牛找工作
题目:
为了找到自己满意的工作,牛牛收集了每种工作的难度和报酬。牛牛选工作的标准是在难度不超过自身能力值的情况下,牛牛选择报酬最高的工作。在牛牛选定了自己的工作后,牛牛的小伙伴们来找牛牛帮忙选工作,牛牛依然使用自己的标准来帮助小伙伴们。牛牛的小伙伴太多了,于是他只好把这个任务交给了你。
输入描述:
每个输入包含一个测试用例。
每个测试用例的第一行包含两个正整数,分别表示工作的数量$N(N\le100000)$和小伙伴的数量$M(M\le100000)$。
接下来的N行每行包含两个正整数,分别表示该项工作的难度$D_i(D_i\le1000000000)$和报酬$P_i(P_i\le1000000000)$。
接下来的一行包含M个正整数,分别表示M个小伙伴的能力值$A_i(A_i\le1000000000)$。
保证不存在两项工作的报酬相同。
输出描述:
对于每个小伙伴,在单独的一行输出一个正整数表示他能得到的最高报酬。一个工作可以被多个人选择。
样例:
in: 3 3 1 100 10 1000 1000000000 1001 9 10 1000000000 out: 100 1000 1001
解析:
N, M都达到了$10^5$,很明显,对于每次询问要采用$O(logn)$或$O(1)$的算法,$O(logn)$可以二分查找,$O(1)$可以通过预处理来达到目标。
因此,先按每个工作的能力值升序排序,这样子可以二分查找到每个同学能做的所有工作,然后再这些工作中找到薪酬最大的;
如何快速找薪酬最大的,这里就要对刚刚升序排序的输出进行区间最大值的预处理了,递推一下就可以得到[1, i]区间的最大值,找区间薪酬最大,只需要访问下dp[i]就行了。
代码:
|
|
第二题:被3整除
题目:
小Q得到一个神奇的数列:
1, 12, 123,...12345678910,1234567891011...。
并且小Q对于能否被3整除这个性质很感兴趣。
小Q现在希望你能帮他计算一下从数列的第l个到第r个(包含端点)有多少个数可以被3整除。
输入描述:
输入包括两个整数
l和r$(1 <= l <= r <= 10^9)$, 表示要求解的区间两端。
输出描述:
输出一个整数, 表示区间内能被3整除的数字个数。
样例:
in: 2 5 out: 3
解析:
看到数据范围就应该明白,这题不能递推,一是数组开不了这么大,二是递推时间很长。因此只能用数学方法算出来(这就是数据范围给我们做题的提示)。
一个数字n如果可以被3整除,$n = a 10^n + b$,那么$a \% 3 + b \% 3 = 0$,1, 2, 3, 4, ...分别对3取模得到1, 2, 0, 1, 2, 0, ...,这个时候再看题中给出的序列,1, 12, 123, 1234, ...是不是可以把其中元素分解成$n = a 10^n + b$,那么可以发现,1, 12, 123, 1234, 12345, ...,能被3整除的如下false, true, true, false, true, true, false, ...,可以发现这个序列以3为周期,因此,代码就可以写出来了。
代码:
|
|
第三题:安置路灯
题目:
小Q正在给一条长度为
n的道路设计路灯安置方案。
为了让问题更简单,小Q把道路视为n个方格,需要照亮的地方用'.'表示, 不需要照亮的障碍物格子用'X'表示。
小Q现在要在道路上设置一些路灯, 对于安置在pos位置的路灯, 这盏路灯可以照亮pos - 1, pos, pos + 1这三个位置。
小Q希望能安置尽量少的路灯照亮所有'.'区域, 希望你能帮他计算一下最少需要多少盏路灯。
输入描述:
输入的第一行包含一个正整数
t$(1 \le t \le 1000)$, 表示测试用例数
接下来每两行一个测试数据, 第一行一个正整数n$(1 \le n \le 1000)$,表示道路的长度。
第二行一个字符串s表示道路的构造,只包含'.'和'X'。
输出描述:
对于每个测试用例, 输出一个正整数表示最少需要多少盏路灯。
样例:
in: 2 3 .X. 11 ...XX....XX out: 1 3
解析:
一开始,我以为障碍物是不能放灯的,故,只要求出连续的.有多少个.(假设sum个),答案就是ceil(sum / 3),于是写出了下面的代码;
|
|
这个题,障碍物是可以放灯的,那么,贪心来搞,首先,对于...来说,我们把灯放在第二个位置上是绝对优于把灯放在第一个位置上的,如果发现当前点是障碍物,不要管它,继续向后走,然后按找上面所说的放灯就行了。
代码:
|
|
第四题:数对
题目:
牛牛以前在老师那里得到了一个正整数数对
(x, y), 牛牛忘记他们具体是多少了。
但是牛牛记得老师告诉过他x和y均不大于n, 并且x除以y的余数大于等于k。
牛牛希望你能帮他计算一共有多少个可能的数对。
输入描述:
输入包括两个正整数
n,k$(1 \le n \le 10^5, 0 \le k \le n - 1)$。
输出描述:
对于每个测试用例, 输出一个正整数表示可能的数对数量。
样例:
in: 5 2 out: 7
解析:
这里我们从k + 1枚举y到n,对于一个确定的y,x % y的值的大小是有周期性的,因此可以直接计算出来,但是对于k = 0要特殊处理,因为对于任意的(x, y),x % y永远大于等于0,因此,当k = 0时,答案为n * n。
代码:
|
|
第五题:矩形重叠
题目:
平面内有
n个矩形, 第i个矩形的左下角坐标为$(x1[i], y1[i])$, 右上角坐标为$(x2[i], y2[i])$。
如果两个或者多个矩形有公共区域则认为它们是相互重叠的(不考虑边界和角落)。
请你计算出平面内重叠矩形数量最多的地方,有多少个矩形相互重叠。
输入描述:
输入包括五行。
第一行包括一个整数n$(2 \le n \le 50)$, 表示矩形的个数。
第二行包括n个整数$x_1i$,表示左下角的横坐标。
第三行包括n个整数$y_1i$,表示左下角的纵坐标。
第四行包括n个整数$x_2i$,表示右上角的横坐标。
第五行包括n个整数$y_2i$,表示右上角的纵坐标。
输出描述:
输出一个正整数, 表示最多的地方有多少个矩形相互重叠,如果矩形都不互相重叠,输出1。
样例:
in: 2 0 90 0 90 100 200 100 200 out: 2
解析:
这个题和线段重叠那个题很像,但是多了一维就不是那么好搞了,这里的n很小,那么肯定就是从这里下手了;
我的第一反应就是随机化算法,即随机生成一个点,然后判断这个点在多少个矩形中,维护一个最大值。但是坐标的范围太大了,因此,要进行离散化,把X轴和Y轴的坐标离散化成小坐标;
但是,这个离散化算法还是有问题,无法处理两个矩形共线或共点!多么希望我们随机化出来的点不在矩形的边界上啊;
注意到,我们离散化出来的坐标都是挨在一起的,例如1后面一定是2,但是如果我们把离散化后的坐标扩大两倍,那么2后面就是4了,中间的3是没有使用的,而单位区域的中心是不会在矩形的边界上的,因此我们可以随机化单位区域的中心,以这个点去判断是否在矩形中,这样就解决了不考虑边界和角落这个条件,而把离散化后的坐标扩大两倍,举个例子,中心就是(2 + 4) / 2 = 3,中心可以确保都是正整数。
代码:
|
|
第六题:迷路的牛牛
题目:
牛牛去犇犇老师家补课,出门的时候面向北方,但是现在他迷路了。虽然他手里有一张地图,但是他需要知道自己面向哪个方向,请你帮帮他。
输入描述:
每个输入包含一个测试用例。
每个测试用例的第一行包含一个正整数,表示转方向的次数N$(N\le1000)$。
接下来的一行包含一个长度为N的字符串,由L和R组成,L表示向左转,R表示向右转。
输出描述:
输出牛牛最后面向的方向,
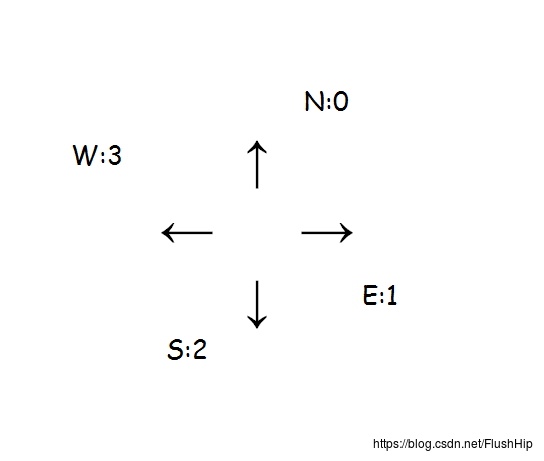
N表示北,S表示南,E表示东,W表示西。
样例:
in: 3 LRR out: E
解析:
如图:
把NESW用数字0123表示,向左走就减一,向右走就加一,由于在处理的过程中ans可能为负数,因此对ans加4再模4。
代码:
|
|
第七题:牛牛的闹钟
题目:
牛牛总是睡过头,所以他定了很多闹钟,只有在闹钟响的时候他才会醒过来并且决定起不起床。从他起床算起他需要
X分钟到达教室,上课时间为当天的A时B分,请问他最晚可以什么时间起床
输入描述:
每个输入包含一个测试用例。
每个测试用例的第一行包含一个正整数,表示闹钟的数量N$(N\le100)$。
接下来的N行每行包含两个整数,表示这个闹钟响起的时间为$H_i(0\le A<24)时M_i(0\le B<60)$分。
接下来的一行包含一个整数,表示从起床算起他需要$X(0\le X\le100)$分钟到达教室。
接下来的一行包含两个整数,表示上课时间为$A(0\le A<24)$时$B(0\le B<60)$分。
数据保证至少有一个闹钟可以让牛牛及时到达教室。
输出描述:
输出两个整数表示牛牛最晚起床时间。
样例:
in: 3 5 0 6 0 7 0 59 6 59 out: 6 0
解析:
把时间全都化成分钟,然后算出牛牛最迟起床时间,在闹钟的时间中二分求上界就行了。
代码:
|
|
第八题:牛牛的背包问题
题目:
牛牛准备参加学校组织的春游, 出发前牛牛准备往背包里装入一些零食, 牛牛的背包容量为
w。
牛牛家里一共有n袋零食, 第i袋零食体积为v[i]。
牛牛想知道在总体积不超过背包容量的情况下,他一共有多少种零食放法(总体积为0也算一种放法)。
输入描述:
输入包括两行
第一行为两个正整数n和w$(1 \le n \le 30, 1 \le w \le 2 * 10^9)$,表示零食的数量和背包的容量。
第二行n个正整数v[i]$(0 \le v[i] \le 10^9)$,表示每袋零食的体积。
输出描述:
输出一个正整数, 表示牛牛一共有多少种零食放法。
样例:
in: 3 10 1 2 4 out: 8
解析:
一看就是最经典“0 - 1背包问题“,但是,背包的容量太大了,会导致数组都开不了,而且还超时。
那么,就枚举呗,枚举使用二进制位运算枚举集合,就写了以下的代码:
|
|
写完之后才意识到$2^{30} \approx 10^9 $,GG,这肯定不行,不过枚举还是必要的,毕竟不能动态规划了,那就少枚举点吧,枚举一半,一半是$2^{15} \approx 10^5$,好像可以,那另一半怎么办,我们可以把第一半枚举出来的和存到数组arr中,然后排序,这样,在枚举另一半的时候可以通过w减去枚举得到的值,结果假设为res,最后利用这个res在arr中二分求上界就可以得到当前状态的答案,维护一个和,这个题就通过了。
代码:
|
|
代码JAVA实现
JAVA的代码和C++的代码差不多,最大的区别就是JAVA中没有lower_bound,upper_bound,这是STL中的两个二分求上下界函数,自己手动实现一下就好了,可以参考你真的理解二分的写法吗 - 二分写法详解。
牛牛找工作
|
|
被3整除
|
|
安置路灯
|
|
迷路的牛牛
|
|
数对
|
|
矩形重叠
|
|
牛牛的闹钟
|
|
牛牛的背包问题
|
|